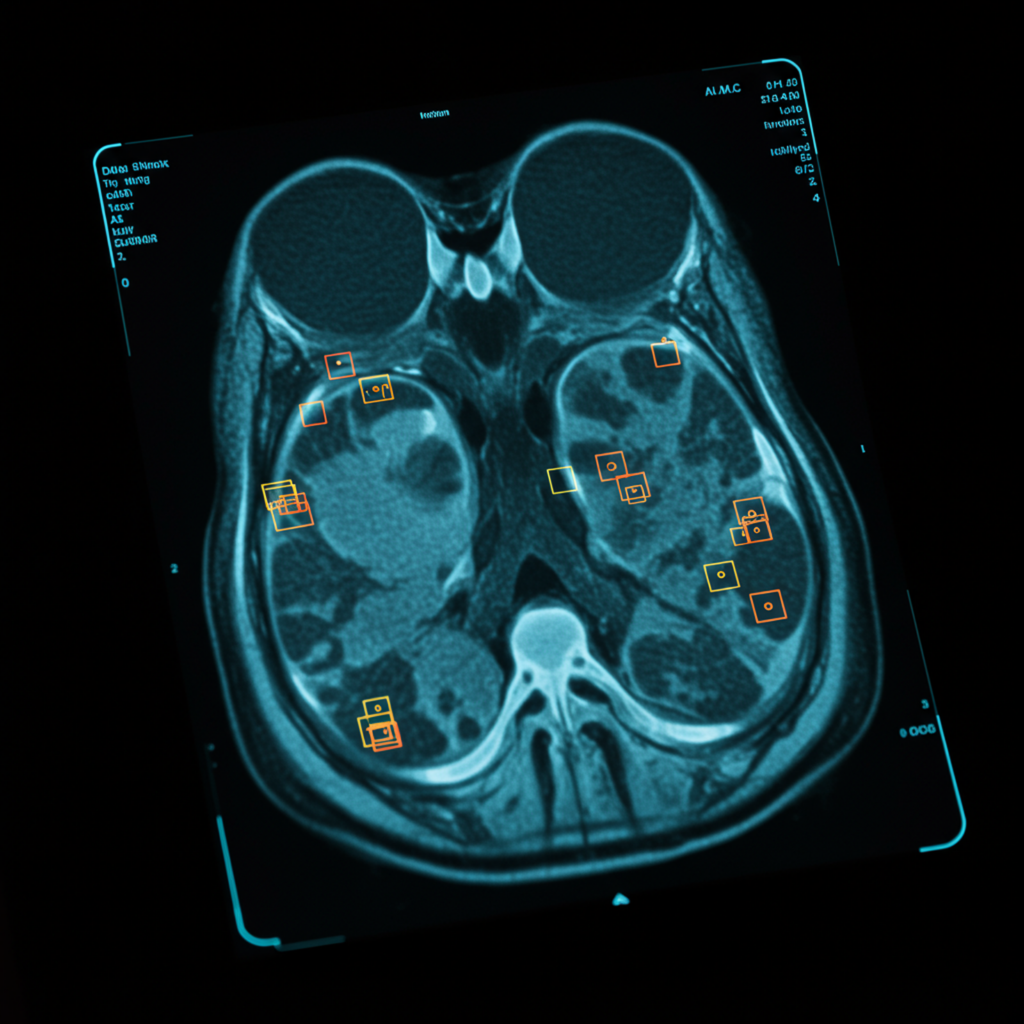
Precise data annotation is the cornerstone of effective AI and machine learning models in medical imaging. The accuracy and reliability of these models directly correlate with the quality of the data they are trained on.
Data Annotation Across Medical Imaging Modalities
Data annotation requirements vary depending on the medical imaging modality and the specific AI application.
1. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI scans provide detailed images of the body’s soft tissues. Annotation tasks may include segmenting tumors (e.g., brain tumors, liver tumors), outlining organs (e.g., liver, kidneys), or labeling specific anatomical structures (e.g., hippocampus in brain scans).
2. CT Scans (Computed Tomography): CT scans use X-rays to create cross-sectional images of the body. Annotation can involve identifying and measuring lung nodules, segmenting organs (e.g., heart, lungs), or detecting bone fractures.
3. X-rays: X-rays are used to visualize bones and dense tissues. Annotation tasks include identifying fractures, diagnosing pneumonia based on lung opacities, or detecting foreign objects.
4. Ultrasound: Ultrasound uses sound waves to create real-time images of internal organs and tissues. Annotation may involve identifying and measuring fetal structures, segmenting the heart, or detecting abnormalities in the liver or other organs.
5. PET Scans (Positron Emission Tomography): PET scans use radioactive tracers to visualize metabolic activity in the body. Annotation tasks can include identifying areas of increased glucose uptake in cancer patients or assessing brain activity.
The Benefits of Expertly Annotated Data:
Expertly annotated data unlocks numerous benefits for healthcare providers:
1. Improved Accuracy: AI models trained on high-quality data achieve higher accuracy in disease detection, leading to fewer false positives and false negatives.
2. Earlier Disease Detection: AI can identify subtle anomalies in medical images that may be missed by human clinicians, enabling earlier diagnosis and treatment.
3. Reduced Diagnostic Errors: AI can provide a second opinion, helping to reduce diagnostic errors and improve patient safety.
4. Faster Development Cycles: Expertly annotated data accelerates the development and deployment of AI technologies, bringing life-saving solutions to market faster.
5. Enhanced Patient Outcomes: By enabling earlier and more accurate diagnoses, AI can contribute to improved patient outcomes, leading to better care and quality of life.